
The section should not be padded to the next boundary. The number of line-number entries for the section. This value is zero for executable images. The number of relocation entries for the section. If there are no COFF line numbers, this value is zero. If there are no relocations, this value is zero.Ī file pointer to the beginning of the line-number entries for the section. If a section contains only uninitialized data, set this member is zero.Ī file pointer to the beginning of the relocation entries for the section. This value must be a multiple of the FileAlignment member of the If the section contains only uninitialized data, the member is zero.Ī file pointer to the first page within the COFF file. If this value is less than the VirtualSize member, the remainder of the section is filled with zeroes. The size of the initialized data on disk, in bytes. For object files, this is the address of the first byte before relocation is applied. The address of the first byte of the section when loaded into memory, relative to the image base. This field is valid only for executable images and should be set to 0 for object files. If this value is greater than the SizeOfRawData member, the section is filled with zeroes. The total size of the section when loaded into memory, in bytes. Executable images do not use a string table and do not support section names longer than eight characters. For longer names, this member contains a forward slash (/) followed by an ASCII representation of a decimal number that is an offset into the string table. There is no terminating null character if the string is exactly eight characters long. Syntax typedef struct _IMAGE_SECTION_HEADER IMAGE_SECTION_HEADER, *PIMAGE_SECTION_HEADER Īn 8-byte, null-padded UTF-8 string. Different organizations may have different formatting procedures, so be flexible in adapting your writing skills.Represents the image section header format. Not all memos will be the same, and the structure can change as you see necessary. This is a suggested distribution of the material to make writing memos easier. Closing Segment, Necessary Attachments: 1/8 of the memo.Summary, Discussion Segment: 1/2 of the memo.Opening, Context and Task: 1/4 of the memo.Sections: The sections of the memo should be allocated in the following manner: Using lists will help you be concise when writing a memo. This will draw the readers' attention to the section and help the audience remember the information better. Use Lists: For easy reading, put important points or details into lists rather than paragraphs when possible. The major headings you choose are the ones that should be incorporated in your purpose-statement in the opening paragraph. For example, instead of using "Summary" for your heading, try "New Advertising Recommendations," which is much more specific. Write headings that are short but clarify the content of the segment. Therefore it is beneficial to use headings and lists to help the reader pinpoint certain information.Īdd Headings: You can help your reader understand your memo better by using headings for the summary and the discussion segments that follow it. Business materials should be concise and easy to read. Instead of using indentations to show new paragraphs, skip a line between sentences.

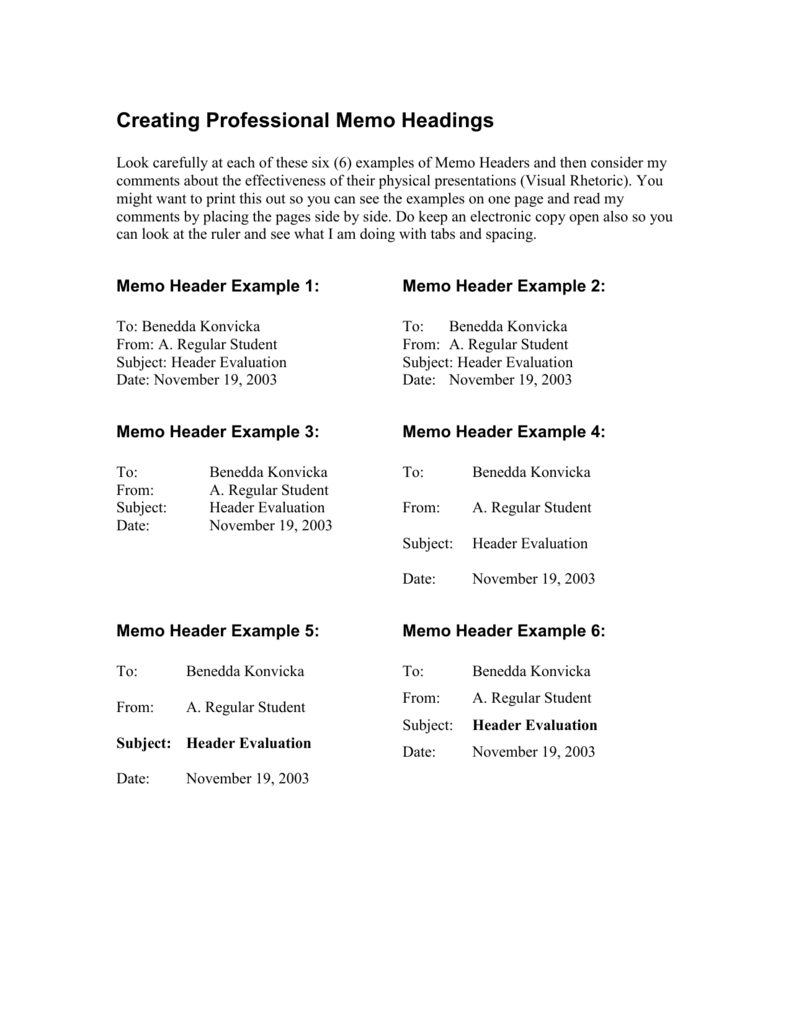
A memo is usually a page or two long, single spaced and left justified.

The format of a memo follows the general guidelines of business writing. This handout will help you solve your memo-writing problems by discussing what a memo is, describing the parts of memos, and providing examples and explanations that will make your memos more effective.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
